Quantum computing is an innovative field that uses the strange rules of subatomic particles to solve problems faster than regular computers. For data scientists, this means new opportunities to tackle complex challenges in machine learning, optimization, and more. With the rise of quantum computing projects, many open-source tools have emerged, making it easier to explore this technology. This article explores the top open-source quantum tools that data scientists can use to get started, offering hands-on experience with simulators, real hardware, and innovative frameworks.
Why Quantum Computing Matters for Data Scientists?
Data scientists work with huge datasets and complex models, often hitting limits with classical computing power. Quantum computing promises to speed up tasks like pattern recognition, optimization, and cryptography. However, the technology is still new, and access to quantum hardware is limited. This is where open-source quantum tools come in, offering free resources to experiment with quantum algorithms and simulations. These tools let data scientists learn the basics, test ideas, and even contribute to the growing community without needing expensive equipment.
The beauty of open-source projects is their accessibility. With just a basic understanding of Python and some math (like linear algebra), you can start exploring. Many projects also include tutorials, documentation, and community support, making them ideal for beginners and experts.
Top Open-Source Quantum Computing Tools for Data Scientists
Let’s explore some of the best quantum computing tools available today.
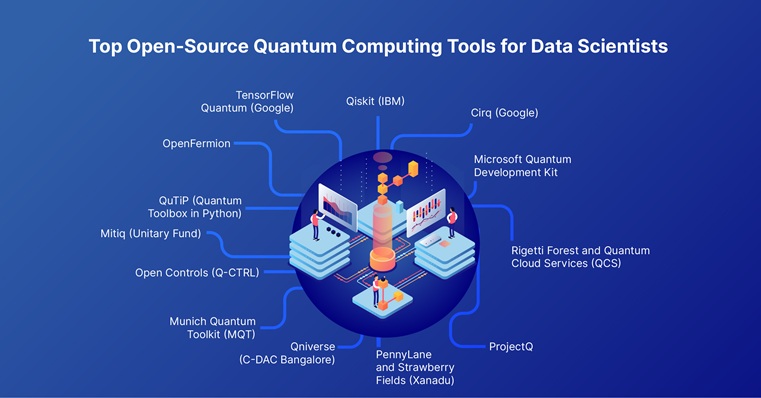
1. Qiskit (IBM)
Qiskit is one of the most popular open-source quantum tools developed by IBM. It’s a comprehensive software development kit (SDK) that lets data scientists design and run quantum circuits, experiment with real quantum hardware, and develop algorithms. The platform supports OpenQASM, a quantum assembly language, and integrates with IBM’s quantum processors via the cloud.
For data scientists, Qiskit offers practical projects like building a quantum random number generator. This uses the Hadamard gate to create a superposition of 0 and 1 states, generating random bitstrings that can be used in simulations or machine learning models. Other projects include Grover’s search algorithm, which speeds up unstructured searches, and Shor’s algorithm for factoring numbers, a potential game-changer for cybersecurity. The Qiskit textbook and video series provide step-by-step guides, while Jupyter notebooks offer hands-on coding examples.
Qiskit’s community is huge, with extensive documentation and forums. You can also explore advanced topics like the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) to find the ground state energy of molecules, a task relevant to chemistry and materials science. You can download it from here and start with the official tutorials.
2. Cirq (Google)
Developed by Google’s AI Quantum Team, Cirq is an open-source quantum tool focused on writing and optimizing quantum circuits for Noisy Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices. It’s built in Python and works with simulators and quantum processors, making it a great choice for data scientists interested in AI applications.
Cirq shines in projects involving quantum machine learning. Its compatibility with OpenFermion-Cirq allows data scientists to tackle chemistry problems, while its alpha release status encourages experimentation. Google’s focus on AI suggests Cirq could evolve to support neural network optimization, a key area for data scientists. The documentation and examples are solid, and you can find the code on GitHub.
3. Microsoft Quantum Development Kit
Microsoft’s Quantum Development Kit (QDK) is an open-source quantum tool featuring Q#, a high-level language designed for quantum programming. It includes simulators, libraries, and integration with classical languages like C# and Python, making it accessible for data scientists used in traditional programming environments.
The QDK is ideal for testing quantum algorithms in a familiar setting. While it has superseded the earlier LIQUi|> software, it retains a focus on optimization and scheduling. You can use it to explore hybrid quantum-classical models, a growing field in machine learning. Download it from here and check the documentation to get started.
4. Rigetti Forest and Quantum Cloud Services (QCS)
Rigetti’s Forest suite is an open-source quantum tool that includes Quil (a quantum instruction language), PyQuil (a Python library), Grove (a program library), and QVM (Quantum Virtual Machine). It provides access to Rigetti’s cloud-based quantum hardware, which is useful for data scientists wanting real-world testing.
PyQuil and Grove are available on GitHub, offering tools to build and simulate quantum programs. QCS co-locates classical computing with quantum hardware, enabling hybrid workflows. You can use this for optimization problems or quantum machine learning, though the community has faced fluctuations due to Rigetti’s financial challenges.
5. ProjectQ
ProjectQ is an open-source quantum tool implemented in Python, offering a flexible framework for quantum programming. It can translate programs to simulators or hardware like IBM’s Quantum Experience, making it versatile for data scientists.
Its FermiLib library is perfect for fermionic quantum simulations, relevant to chemistry and physics. ProjectQ’s intuitive syntax and future hardware support make it a good choice for experimenting with new algorithms. Find more at the ProjectQ website.
6. PennyLane and Strawberry Fields (Xanadu)
Xanadu’s PennyLane is an open-source quantum tool for quantum machine learning and optimization, integrating with TensorFlow and PyTorch. It supports continuous-variable photonic technology and gate-based platforms like ProjectQ and Qiskit, appealing to data scientists in AI.
Strawberry Fields, also from Xanadu, focuses on simulating photonic quantum circuits, ideal for quantum information processing. Together, they offer a full stack for designing and optimizing quantum models. Explore them at Xanadu’s website.
7. Qniverse (C-DAC Bangalore)
Qniverse is an open-source quantum tool designed to make quantum computing accessible. Developed by C-DAC Bangalore, it provides an integrated environment for designing, simulating, and executing quantum algorithms, with support for HPC systems and accelerators like GPUs.
You can use Qniverse to scale simulations, making it suitable for large datasets. Its focus on usability and performance is a plus, though it’s still emerging. Check C-DAC’s website for details.
8. Munich Quantum Toolkit (MQT)
The Munich Quantum Toolkit (MQT) from the Technical University of Munich offers open-source quantum tools for design automation across the quantum software stack. It includes solutions for simulation, compilation, verification, and error correction.
You can leverage MQT for optimizing quantum circuits, a key task in machine learning. Its open-source nature and GitHub hosting encourage community contributions. Find it on GitHub.
9. Open Controls (Q-CTRL)
Q-CTRL’s Open Controls is an open-source quantum tool providing error-robust quantum control protocols in Python. It aims to be a comprehensive library of tested techniques, deployable on various hardware.
For data scientists, this is useful for mitigating noise in quantum experiments, enhancing the reliability of machine learning models. More info is on Q-CTRL’s website.
10. Mitiq (Unitary Fund)
Mitiq is an open-source quantum tool for error mitigation, compatible with Qiskit, Cirq, and PyQuil. It uses techniques like zero-noise extrapolation to reduce errors on noisy devices.
You can apply Mitiq to improve simulation accuracy, a critical need for quantum machine learning. Find it on GitHub.
11. QuTiP (Quantum Toolbox in Python)
QuTiP is an open-source quantum tool for simulating open quantum systems, widely used in quantum physics and information research. It relies on Numpy, Scipy, and Matplotlib for numerical and graphical output.
You can use QuTiP to model quantum dynamics, relevant to optimization and machine learning. It’s free for all platforms and available on GitHub.
12. OpenFermion
OpenFermion is an open-source quantum tool for quantum chemistry, generating equations for chemical systems interpretable by quantum computers. It integrates with classical chemistry packages and quantum frameworks like Rigetti Forest.
Data scientists in chemistry or materials science can use it to explore molecular properties. Download it from GitHub.
13. TensorFlow Quantum (Google)
TensorFlow Quantum (TFQ) is an open-source quantum tool for hybrid quantum-classical machine learning, integrating Cirq with TensorFlow APIs. It focuses on quantum data and high-performance simulators.
You can use TFQ to prototype ML models, leveraging Google’s expertise. Find it on GitHub.
Getting Started with These Tools
Follow these simple steps to get started:
- Check out the official documentation for each tool. Most quantum computing projects provide easy guides on how to set them up.
- Use the installation instructions in the documentation. Since most tools are Python-based, you can install them using commands like pip on your computer.
- Begin with beginner-friendly tasks. Try building a quantum random number generator or experimenting with Grover’s algorithm. Use the tutorials provided with the tools to guide you.
- Work through the step-by-step tutorials available for each project. They’ll help you understand the basics and get hands-on practice.
- Sign up for GitHub or forums related to these tools. Connect with other learners and experts to ask questions and share ideas.
- Work with the community to solve problems and improve your skills. These connections will help you grow in this transformative field.
Conclusion
The world of quantum computing is opening up for data scientists through these open-source quantum tools. From Qiskit’s comprehensive ecosystem to Mitiq’s error mitigation, each project offers unique opportunities to explore quantum computing for data scientists. By engaging with these resources, you can contribute to a field that’s set to revolutionize technology. Start today and be part of the quantum future!